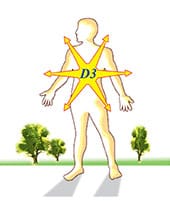
MORE RESEARCH IS REVEALING THE MANY IMPORTANT FUNCTIONS OF VITAMIN D.
MOST Caucasians deem the act of using an umbrella to protect us from the sun as weird. In tropical Malaysia, many women use umbrellas to protect themselves from the sun. Over here, if you tried giving a see-through umbrella to a fair-skinned lady, she would think you were being ridiculous.
Most women pride themselves on their flawless, porcelain complexion, and are willing to spend hundreds upon thousands of ringgit to attain it – from sunblock up to SPF 50 to creams, lotions and serums for lightening pigmentation, freckles and acne scars, as well as facial packages that range from peeling to whitening, and even microdermal abrasion.
Other people who stay clear of the sun or slap on sunblock are afraid of skin cancer, although there is no evidence that regular, moderate sun exposure causes melanoma. In fact, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has observed that melanoma is seen more often in people who do not have regular, moderate sun exposure, than in those who regularly spend time in the sun.
SUNSHINE AND SKIN CANCER (MELANOMA) PREVENTION
This is an important point, because if you are shunning the sun for fear of skin cancer, you are, ironically, missing out on one of the most potent natural cancer protections available.
Vitamin D’s protective effect against cancer works in multiple ways, including:
Increasing the self-destruction of mutated cells (which, if allowed to replicate, could lead to cancer).Reducing the spread and reproduction of cancer cells.Causing cells to become fully differentiated (cancer cells often lack differentiation).Reducing the growth of new blood vessels from pre-existing ones, which is a step in the transition of dormant tumours turning into cancerous ones.
You may be depriving yourself of this important cancer-protective nutrient – vitamin D3 – if you shy away from the sun.
According to the Vitamin D Council, more than 50% of the world’s population is at risk of vitamin D3 deficiency. Vitamin D is required by the body for many important health functions, from strengthening the immune system to controlling cell growth.
Every tissue in the body, including the brain, heart, breast, muscles and immune system has receptors for vitamin D, meaning that it is needed at optimal levels for these tissues to function properly, and for general well-being.
As we are on the topic of cancer, let’s learn how vitamin D deficiency is linked to 18 types of cancer.
VITAMIN D3 AND CANCER PREVENTION
One of the most impressive and rapid growing areas of vitamin D research is in the area of cancer prevention. Over 90 studies have described how higher levels of vitamin D reduce cancers of the breast, prostate, colon, oesophagus, pancreas, ovary, rectum, bladder, kidney, lung and uterus, as well as non-Hodgkins lymphoma and multiple myeloma.
Optimal levels of vitamin D reduce risk of:
Breast cancer
Vitamin D may play a role in controlling normal breast cell growth, and may be able to stop breast cancer cells from growing.
A study coming out of Canada indicates that vitamin D may play a pivotal role in the progressive nature of breast cancer. This study found that women who are deficient in vitamin D at the time of breast cancer diagnosis are 75% more likely to die from the disease and have a 94% higher risk of having the cancer spread, compared to women with sufficient/optimal levels of vitamin D in their body.
Another study was conducted by researchers from the University of Rochester Medical Centre, which examined vitamin D levels in 155 breast cancer patients in the months before or after they had surgery to treat their disease. They found suboptimal vitamin D levels to be highly predictive of the presence of biological markers associated with more aggressive tumours.
In yet another recent study published in the May 2012 issue of Carcinogenesis, a group of scientists from the Catholic University Leuven in Belgium evaluated the relationship between vitamin D status and breast cancer. They wanted to know if vitamin D status at the time of diagnosis correlates or influences tumour characteristics, survival, and cancer relapse.
They found that low levels of vitamin D were associated with larger tumours (at the time of the diagnosis), and high levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels were associated with smaller breast tumours. This is an important finding, as previous studies did not show the link between vitamin D levels and tumour size.
Prostate cancer
Vitamin D may turn out to be a ray of hope for men with prostate cancer. Vitamin D does not protect men from getting prostate cancer, but it may lessen their chances of dying from it.
In a new study, men with the highest levels of vitamin D in their blood were 57% less likely than men with the lowest levels to succumb to prostate cancer.
One prostate cancer study showed that patients who received 2,000 IU of vitamin D3 a day had a 50% reduction in the rise of their PSA (prostate-specific antigen) levels, which is an indicator of prostate cancer activity.
Colorectal cancer
Researchers in Europe have found that people with abundant levels of vitamin D have a much lower risk of colon cancer. The findings add to a growing body of evidence that suggest vitamin D may have the ability to help prevent colon cancer, and possibly even improve survival in those who have the disease.
For the current study, researchers looked at the link between blood levels of vitamin D, as well as dietary vitamin D and calcium, and who was at risk for colorectal cancer. They based their findings on information from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer Study (EPIC), a study of more than 520,000 people from 10 Western European countries.
They discovered that those with the highest blood levels of vitamin D had a nearly 40% decrease in colorectal cancer risk, than those with the lowest levels.
To find out more about the benefits of vitamin D and cancer, you can go to YouTube on the internet and type in the following:
Vitamin D & Cancer – current trial and evidence, Carole Baggerly.Vitamin D Prevents Cancer. Is It True? UCtelevisionIf you or your loved ones lack sunlight exposure, regularly wear long-sleeved clothing, are confined indoors, or use sunblock when outdoors, you will lack the sunshine vitamin, D3.
But remember, you can still get its benefits in tablet form, without the UV rays and the heat.
References:
- Hatse S, Lambrechts D, Verstuyf A, Smeets A, Brouwers B, et.al – Vitamin D status at breast cancer diagnosis: correlation with tumor characteristics, disease outcome, and genetic determinants of vitamin D insufficiency. Carcinogenesis. 2012 Jul;33(7):1319-26. Epub 2012 May 23.
- Michael F. Holick-Vitamin D and Sunlight: Strategies for Cancer Prevention and Other Health Benefits. Department of Medicine, Section of Endocrinology, Nutrition, and Diabetes, Vitamin D, Skin and Bone Research Laboratory, Boston University Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts. CJASN September 2008 vol. 3 no. 5 1548-1554.
- Grant WB, Holick MF. Benefits and requirements of vitamin D for optimal health: a review. Altern Med Rev. 2005 Jun; 10(2):94-111.
- van den Bemd GJ, Chang GT. Vitamin D and vitamin D analogs in cancer treatment. Curr Drug Targets. 2002 Feb;3(1):85-94.
- Gorham ED, Garland CF, Garland FC, et al. Vitamin D and prevention of colorectal cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2005 Oct;97(1-2):179-94.
- Lou YR, Qiao S, Talonpoika R, Syvala H, Tuohimaa P. The role of Vitamin D3 metabolism in prostate cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2004 Nov;92(4):317-25.